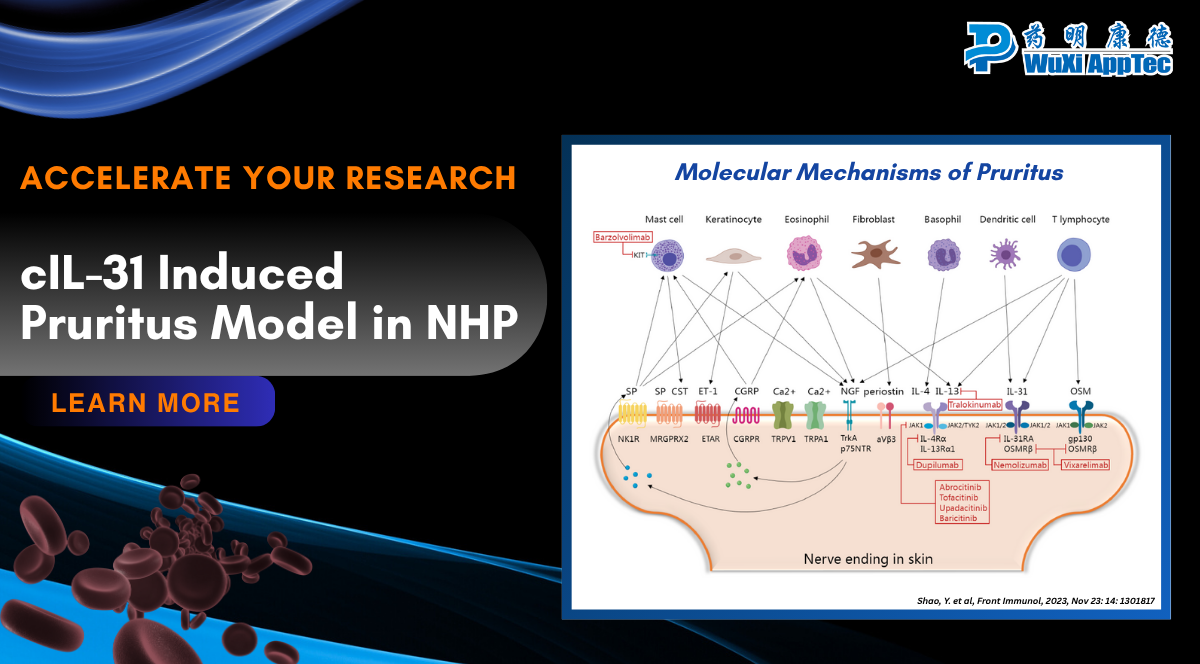
Induced Pruritus Model in NHP
The “itch-scratch cycle” is a central pathogenic driver in many pruritic (itch-related) inflammatory skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis (AD),...
Continue Reading
The “itch-scratch cycle” is a central pathogenic driver in many pruritic (itch-related) inflammatory skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis (AD),...
Continue Reading
Introduction Endometriosis is a common gynecological condition that significantly impacts the health of women of reproductive age worldwide. Approximately 10%...
Continue Reading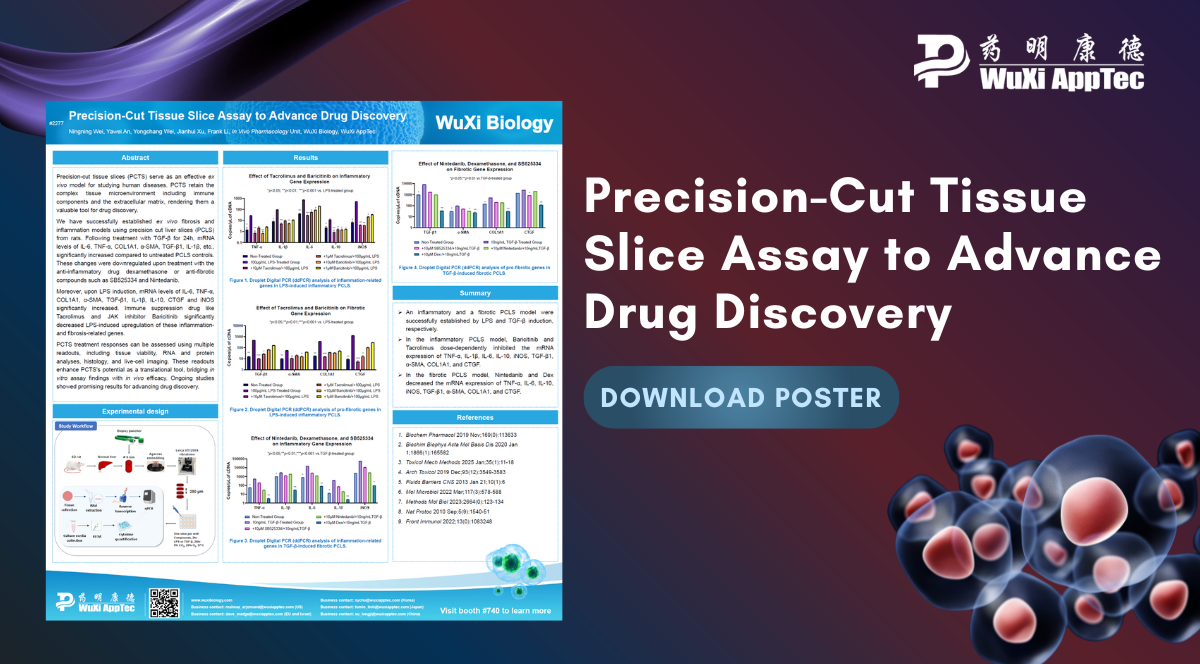
Precision-cut tissue slices (PCTS) are an effective ex vivo model for studying human diseases, including those involving the tissue microenvironment....
Continue Reading
Gout is a common type of inflammatory arthritis caused by elevated uric acid levels in the blood. When uric acid...
Continue Reading
From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Innovations Introduction: Membranous nephropathy (MN) has received particular attention among autoimmune kidney disease due to its...
Continue Reading
Systemic sclerosis (also known as scleroderma) is a chronic autoimmune disease that leads to the buildup of scar tissue in...
Continue Reading
Introduction In recognition of International Women’s Day, we spotlight women’s health—a continuously evolving global healthcare issue. The year 2025 marks...
Continue Reading
Introduction: Women spend about one-third of their lives in menopause or post-menopause, a period that marks the gradual decline of...
Continue Reading
Kidney diseases are complex conditions caused by a variety of factors, including autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders, infections, drug side effects,...
Continue Reading