Innovative Fibrosis Medicine Discovery

Fibrosis, characterized by tissue scarring, is usually chronic and progressive as clinical symptom. It could be caused by diseases, iatrogenic injury or trauma. Those fibrosis-associated diseases include cirrhosis (LF), hepatitis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), chronic kidney disease (CKD), myocardial infarction, heart failure, diabetes, celiac disease, scleroderma, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), and more. The relevant abnormalities affect about one fourth of the world’s population but there have been no effective drugs available until recently. The establishment and application of animal models related to human diseases have attracted more and more of the industry’s attention and has become an indispensable part in pathogenesis research and therapeutic drug discovery.
Our fibrosis models cover liver fibrosis, lung fibrosis, kidney fibrosis, skin fibrosis, peritoneal fibrosis, ocular retinal fibrosis, etc… All pathology and biochemical endpoints are relevant to those that appeared as the clinical characteristics. With the advantage of assay technology, especially qPCR, ELISA, western blotting, flow cytometry, LC-MS/MS, etc., the mechanism of drug action and biomarkers can be evaluated at both protein and gene levels.
Liver Fibrosis
- Chemical induction
- Metabolic induction
- Surgery
Mouse | Rat
IN VIVO PHARMACOLOGY CATALOG
| Liver Fibrosis Model | Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induction |
| Liver Fibrosis Model | Thioacetamide (TAA) induction |
| Liver Fibrosis Model | High-fat & cholesterol diet (HFCD) induction, with hyperlipidemia |
| Liver Fibrosis Model | Diet and CCl4-induced liver fibrosis |
| Liver Fibrosis Model | Diet and STZ-induced pulmonary fibrosis |
| Liver Fibrosis Model | N-nitrosodiethylamine (DEN)-induced liver fibrosis |
| Liver Cirrhosis Model | Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induction |
| Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) Model | Biliary duct ligation (BDL) |
| Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Model | 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine (DDC) induction |
Case Studies
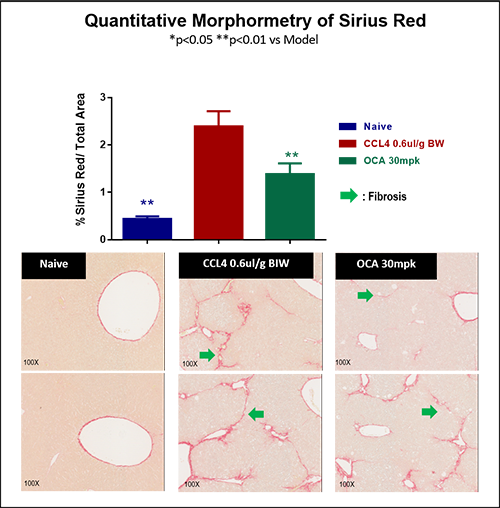
CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice
CCl4-induced liver fibrosis model in C57/BL6J mice is well-recognition and widely used. Based on the requirement from our clients, WuXi Biology has provided a variety of models with different single dose treatment cycle, from 4 weeks up to 20 weeks, with the different CCl4-induced dose ranges by co-induction with the specific diets. We have accumulated much practical experience for clients during compound efficacy evaluation for liver fibrosis.
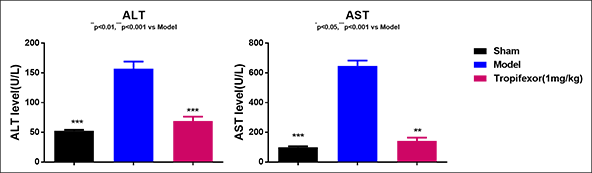
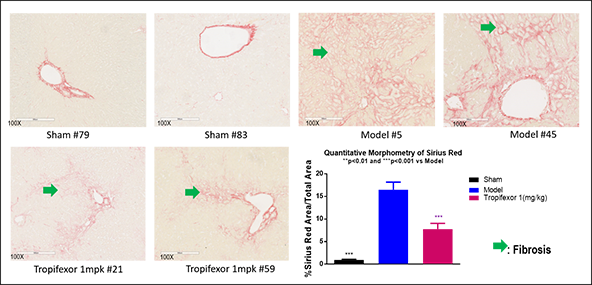
Bile duct ligation (BDL)-induced liver fibrosis in rats
This BDL induced model in SD rats, has been widely used for severe liver fibrosis. Based on the requirements from clients, we refined the surgical steps of bile duct ligation (BDL) and reduced the mortality rate to 10%. This was superior to the mortality rate (50%), which was reported in the literature. The reference drug, Tropifexor, showed good efficacy.
IN VIVO PHARMACOLOGY CATALOG
| Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Models (IPFM) | Bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis |
| Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Models (IPFM) | Silica-induced lung fibrosis |
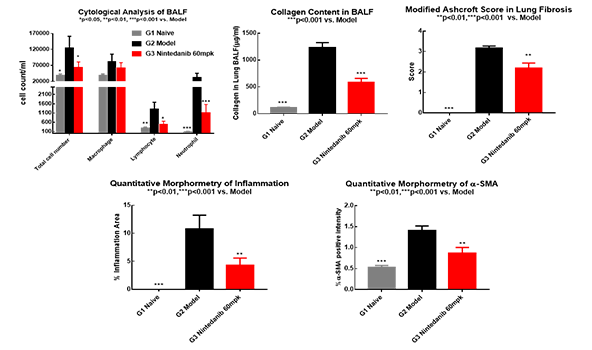
Bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis model in mice
BLM-induced fibrosis in C57/BL6J mice is widely used and very popular for the research in pulmonary fibrosis. After optimization, the mortality of the model was improved and reduced significantly to <10% compared to the literature which is 30-50%. The reference drug, Nintedanib, showed good efficacy.
Renal Fibrosis
- Surgery
- Chemical induction
Mouse | Rat
IN VIVO PHARMACOLOGY CATALOG
| Induced Renal Fibrosis Models (IRFM) | Unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis |
| Induced Renal Fibrosis Models (IRFM) | 5/6 nephrectomy-induced renal fibrosis |
| Induced Renal Fibrosis Models (IRFM) | Purine-induced renal fibrosis |
Others Fibrosis Models
- Chemical induction
Mouse | Rat
IN VIVO PHARMACOLOGY CATALOG
| Induced Skin Fibrosis Models (ISFM) | Silica-induced skin fibrosis model |
| Induced Peritonal Fibrosis Models (IPFM) | Chlorhexidine gluconate-induced peritoneal fibrosis model |
| Induced Ocular Retinal Fibrosis Model (IORFM) | Sodium iodate (NaIO3)-induced retinalfubrosis in mice |
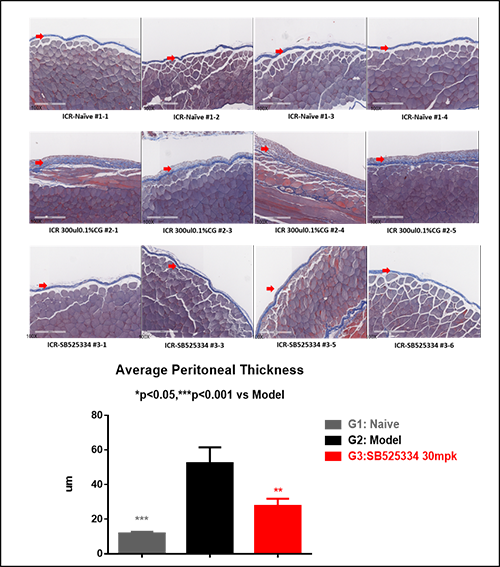
Peritoneal fibrosis model induced by chlorhexidine gluconate in mice
By using ICR mice, this model has been recognized and widely used for peritoneal fibrosis. Its stability and high reliability have been demonstrated through our work with clients. See below for typical data after the treatment with TGFβ inhibitors.
Test Parameters
Mouse | Rat
| Animal characteristics |
| Body weight, tissue weight |
| Liver, lung, kidney, eye function and biomarker analysis |
| Determination of hydrooxyproline and/or collagen content |
| Gene expression (QT-PCR, Microarray, etc.) |
| Protein and metabolite profiling (WB, ELISA, mass spectrometry, etc.) |
| Pathological analysis |
| H&E staining/Analysis in tissues |
| Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) staining for “Glomerulosclerosis Assessment” |
| Collagen deposition evaluation in tissues by “Picrosirius Red” staining and/or “Mason Trichrome” staining |
| Tissue a-SMAIHC staining and quantification |
| Other relavant IHC stains and makers for specific targets, i.e. collagen subtypes, macrophage intersital infiltrates and other downstream signaling biomakers |
in vitro cell culture models
In addition to animal models, we have also established in vitro cell models by using human and rodent cells, either primary fibroblast cells or cell line. It becomes more feasible, cost effective, and allows for greater throughput using a in vitro platform for drug screening and evaluation.
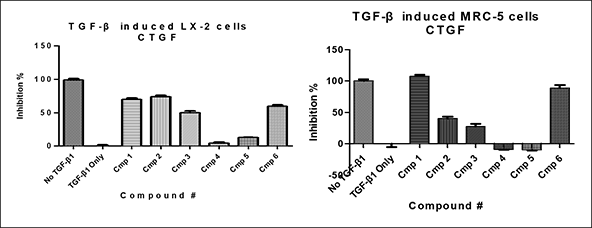
If you’re interested in the field of fibrotic disease models, please don’t hesitate to contact us and connect with our experts for further scientific discussions.

