Comprehensive Kidney Disease Models
In recent years, acute kidney injury (AKI) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are becoming more prevalent. They cause patient suffering, result in mortality, and require prolonged treatment times. Due to the limited understanding of the disease pathogenies and the lack of suitable disease models, the discovery and development of therapeutic products in this area encounter many challenges.
With over 15 years of experience, WuXi Biology has successfully developed and validated a comprehensive collection of clinically relevant rodent models representing AKI, CDK and Kidney fibrosis (KF). In addition to drug efficacy evaluations, the valuable MOA and biomarker information at protein and gene levels can also be provided by multiple endpoints including qPCR, ELISA, WB, FACS, LC-MS, and more.
Acute Kidney Injury
Acute Kidney Injury Models
| Acute Kidney Injury | Cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury model |
| Acute Kidney Injury | LPS-induced acute kidney injury model |
| Acute Kidney Injury | PAN-induced renal podocyte injury model |
| Renal Ischemia | Unilateral renal ischemia & reperfusion |
| Renal Ischemia | Bilateral renal ischemia & reperfusion |
| Acute Kidney Injury | IgA nephropathy-induced by anti-thy1 antibodies |
Cisplatin-induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
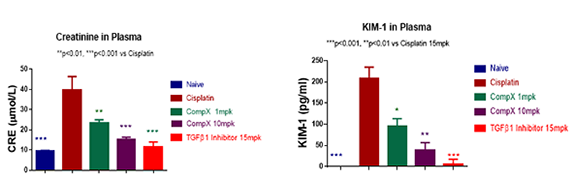
It is well studied that many patients develop severe renal complications after prolonged treatment with Cisplatin. In the Cisplatin-induced AKI model, plasma creatinine and KIM-1 significantly increased in mice treated with Cisplatin. Similar results were seen in patients. The increased creatinine and KIM-1 levels induced by Cisplatin are reversed by TGF-β1 inhibitors.
Nephrotic Syndrome
IN VIVO PHARMACOLOGY CATALOG
| Minimal Change Disease/ Glome Model | Puromycin aminonucleoside (PA) induction |
| Membranous Nephritis Model | Passive Heymann nephropathy, Fx1A antibody induction |
Chronic Kidney Diseases
Chronic and progressive nephropathy models
| Hypertension Model | Deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA) salt induction |
| Chronic Kinney Damage Model | 5/6 nephrectomy |
| Nephropathy Model | Doxorubicin (DOX) induction |
| Kidney Fibrosis | Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis |
| Renal Anemia Model | Adenine-induced chronic and progressive nephropathy |
UUO-induced Kidney Fibrosis Model
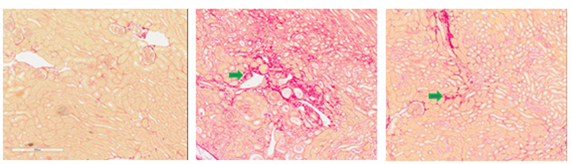
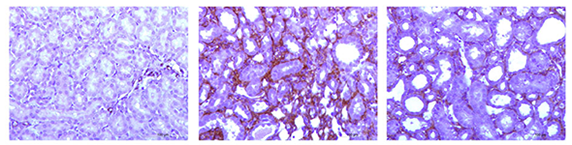
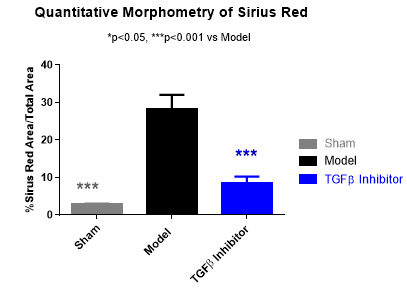
Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction (UUO) causes renal fibrosis and tubular injury as a result of obstructed urine flow. The UUO-induced renal fibrosis model in rats and mice have been widely used for studying kidney fibrosis due to their clinical relevance and utility in testing drug efficacy. As shown in Figure 3, a TGF-β1 inhibitor is shown to reverse the UUO-induced fibrosis, measured by Sirius Red staining (Fig. 3a), smooth muscle actin staining (Fig. 3b) and quantitative measurement of Sirius Red staining (Fig. 3c).
Diabetic Nephropathy
Chronic and progressive nephropathy models
| Diabetic Nephropathy Model | db/db mouse |
| Diabetic Nephropathy Model | BTBR ob/ob mouse |
| Diabetic Nephropathy Model | KK-Ay mouse |
| Diabetic Nephropathy Model | Streptozotocin (STZ) induction |
BTBR ob/ob Diabetic Nephropathy
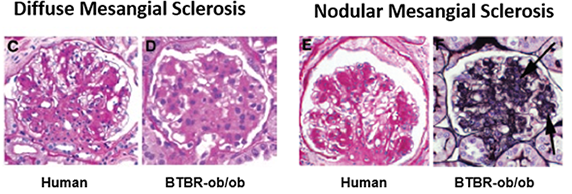
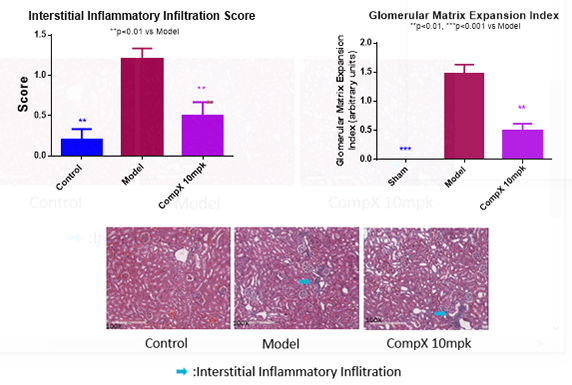
The mouse strain BTBR with the ob/ob leptin-deficiency mutation develops severe type 2 diabetes and morphologic renal lesions which are characteristics of early and advanced diabetic nephropathy (DN) in humans as shown in Figure 2a. In Figure 2b, Compound X significantly suppressed the inflammation (left) and the Glomerular Matrix Expansion Index (right) in the BTBR ob/ob model.
Test Parameters
Mouse | Rat
| Animal characteristics |
| Body weight, tissue weight, food/water intake and metabolic evaluation |
| Kidney function and biomarker analysis |
| Proteinuria: serum creatinine and BUN |
| Serum KIM-1 and other renal tubular biomarkers |
| Determination of hydrooxyproline and/or collagen content |
| Gene expression (qPCR, Microarray, RNA-seq, etc..) |
| Protein and metabolite profiling (WB, ELISA, mass spectrometry, etc.) |
| Pathological analysis |
| H&E staining/Analysis in tissues |
| Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) staining |
| Collagen deposition evaluation in tissues by “Mason Trichrome” staining |
| Tissue a-SMAIHC staining and quantification |
| IHC stains and makers for specific targets, i.e. collagen subtypes, macrophage intersital infiltrates and other downstream signaling biomakers |
In Vitro Kidney Disease Models
In addition to in vivo animal models, the in-vitro cell models of kidney disease and fibrosis, including primary cells or cell lines, also play important roles in efficacy evaluation. Combined with our integrated in-vitro assay platform, the feasible, cost efficient and high throughput options are offered for compound screen and MOA study.
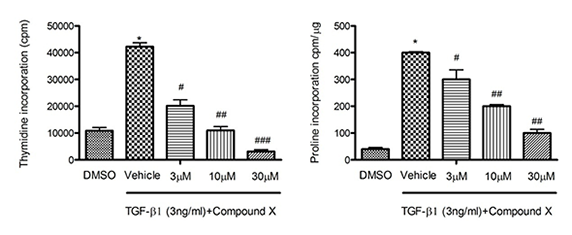
Figure 4 has demonstrated the anti-proliferative (left) and anti-fibrotic (right) effects of Compound X in vitro when the cells were stimulated by TGF-β1.