OncoWuXi Express: Large-scale Cell Panel Screening Platform for Integrated Pharmacogenomics and Bioinformatics Research
Introduction:
OncoWuXi Express will continue to keep you informed about updates to our on-line tumor model database (OncoWuXi Database), as well as our recent progress in cancer and autoimmune research. In this issue, we showcase our large-scale cell panel screening platform for integrated pharmacogenomics and bioinformatics research.
Cell viability assessment is a commonly used in vitro screening method for anti-cancer drug development. The practice of testing innovative anti-cancer compounds across a comprehensive cell panel representing genetic diversity derived from different cancer tissues and organs is increasingly considered a cornerstone of preclinical drug discovery. The Oncology-Immunology team from WuXi Biology has amassed a cell bank encompassing over 600 cell lines across more than 50 cancer types. To augment the multi-technological platforms of pharmacogenomics, these cell lines have been sequentially profiled with RNA-Seq analysis, which includes gene expression quantification, gene fusion detection, MHC typing, and variant splicing expression analysis. This approach aids in the discovery of drug sensitivity related genomic characteristics and mechanisms. We have prioritized 7 types of cell screening panels (Table 1) and we periodically conduct compound screening and testing services, achieving an optimal balance of cost, price, speed, and quality. Researchers can choose the appropriate cell screening panel(s) for compound testing according to experimental needs.
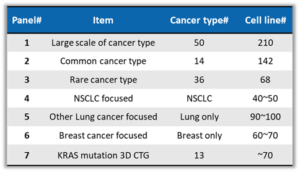
Table 1. Cell Screening Panels
Based on the anti-proliferative activity data of different cell screening panels, we can address the following key challenges through drug bioinformatics analysis:
- Analyze the potential drug-sensitive and non-sensitive types of cancer, predicting clinical indications.
- Analyze the correlation between specific gene expression or mutations and drug efficacy, predicting biomarkers
- Identify compounds with similar pharmacological effects
- Assist in analyzing and verifying the mechanisms of drug action, revealing the targeting of drugs
After integrating bioinformatics analysis from pharmacogenomics, cell panel screening services can be more widely and systematically applied to various aspects of the drug discovery and development process, such as identification of novel anti-cancer targets, the study of drug sensitivity and resistant mechanisms, assessment of in vitro structure activity relationships (SAR) and in vivo model design. This screening approach can also provide evidence for the discovery of clinical biomarkers in drug development, PCC translation for suitable clinical indications, as well as drug combination strategies (Figure 1).
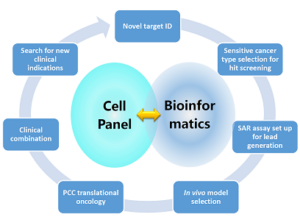
Figure 1. Cell panel screening combined with bioinformatics analysis in pharmacogenomics
Case study: Cell panel screening combined with bioinformatics analysis
Nutlin-3a is a known MDM2inhibitor that can disrupt the binding of MDM2 and the p53 protein, leading to activation of the p53 pathway and achieving anti-cancer functions [1-2]. The Bioinformatics team from WuXi Biology identified Nutlin-3a associated biomarkers and performed unsupervised hierarchical clustering profiling by combining genomic features and drug response data in over 150 cancer cell lines (Figure 2) [3].
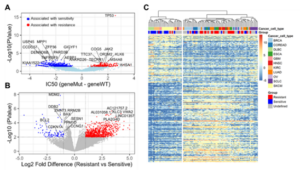
Figure 2. Gene mutation analysis in cell lines (A), differential expression analysis (B), and cluster analysis (C)
Conclusions:
The results show that TP53 gene mutations strongly correlated with Nutlin-3a resistance in cells (Figure 2A). Changes in the expression of MDM2 and TP53 signaling pathway-related genes (including BCL2, BAX, and DDB2) in cell lines are related to drug resistance (Figure 2B). Unsupervised cluster analysis results indicated that DLBCL cells are relatively sensitive to Nutlin-3a, which provides an effective reference for classification of cancer indications (Figure 2C).
References
- Tovar, Christian et al. Small-molecule MDM2 antagonists reveal aberrant p53 signaling in cancer: implications for therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(6):1888-1893.
- Vuaroqueaux, Vincent et al. Pharmacogenomics characterization of the MDM2 inhibitor MI-773 reveals candidate tumors and predictive biomarkers. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021;5(1):96.
- Iorio F, Knijnenburg TA, Vis DJ, et al. A Landscape of Pharmacogenomic Interactions in Cancer. Cell. 2016;166(3):740-754.
WuXi AppTec | Oncology Platform:
- Cancer Cell Panel & In Vitro Oncology Assays; click HERE to learn more
- View our OncoWuXi database by clicking HERE
- Click HERE to view our comprehensive panel of tumor models
Related Content
Despite the success of delivery technologies such as lipid nanoparticles and trivalent GalNAc conjugation, targeted delivery of oligonucleotides to extra...
VIEW RESOURCEWuXi AppTec scientists contributed to a research article in the journal Translational Medicine Communications which characterized the antitumor immune responses...
VIEW RESOURCE
