NLRP3 Inhibitor Reverses Melanoma-Induced Vitiligo
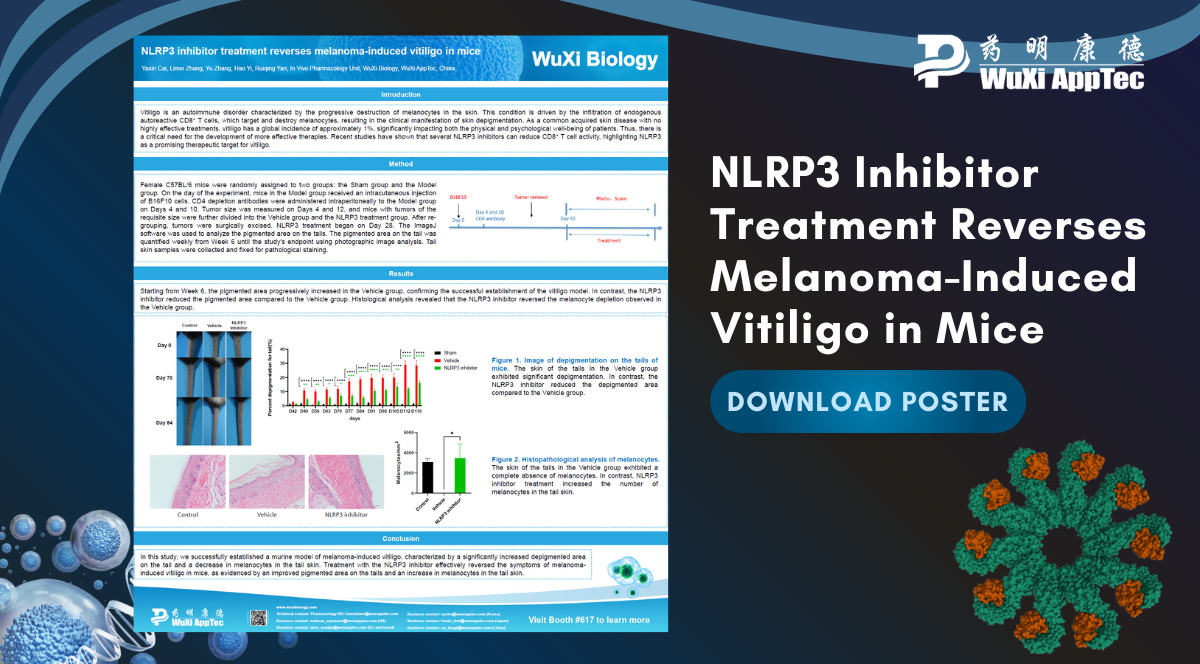
Vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the progressive destruction of melanocytes in the skin. This condition is driven by the infiltration of endogenous autoreactive CD8+ T cells, which target and destroy melanocytes, resulting in the clinical manifestation of skin depigmentation. As a common acquired skin disease with no highly effective treatments, there is an urgent need for the development of more effective therapies.
Recent studies have shown that NLRP3 inhibitors can reduce CD8+ T cell activity, highlighting NLRP3 as a potential target for treating vitiligo. At SITC 2024, WuXi AppTec presented a poster showcasing the successful establishment of an in vivo mouse model to support research in this area. The authors demonstrate that treatment with an NLRP3 inhibitor effectively reversed the symptoms of melanoma-induced vitiligo in mice.

Poster_SITC-2024_NLRP3 inhibitor treatment reverses melanoma-induced vitiligo
Related Content
Introduction Endometriosis is a common gynecological condition that significantly impacts the health of women of reproductive age worldwide. Approximately 10%...
VIEW RESOURCEPrecision-cut tissue slices (PCTS) are an effective ex vivo model for studying human diseases, including those involving the tissue microenvironment....
VIEW RESOURCE
