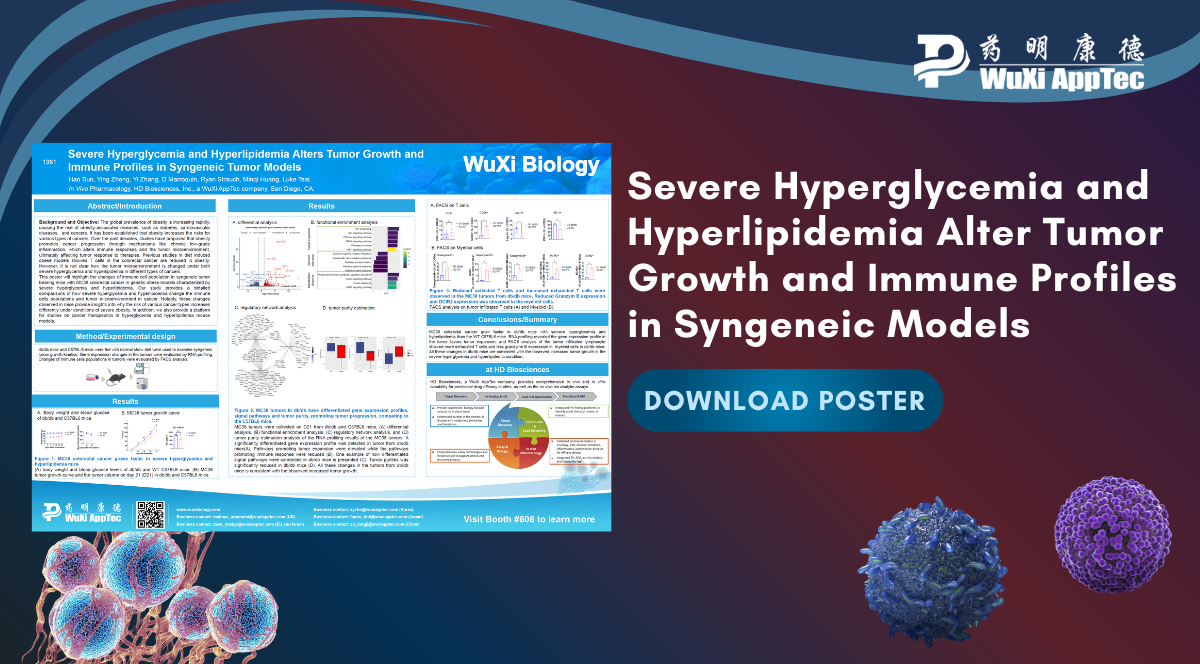
Severe Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipidemia Alter Tumor Growth and Immune Profiles in Syngeneic Tumor Models
Studies have demonstrated that obesity can promote cancer progression through mechanisms that include chronic low-grade inflammation. Previous research with diet-induced...
Continue Reading