Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a serious, chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by a heterogeneous clinical presentation, in which various organs and systems are affected in different ways and with varying degrees of severity. SLE is characterized by an autoimmune reaction involving the innate and adaptive immune systems, including dendritic cells, T cells, and B cells.
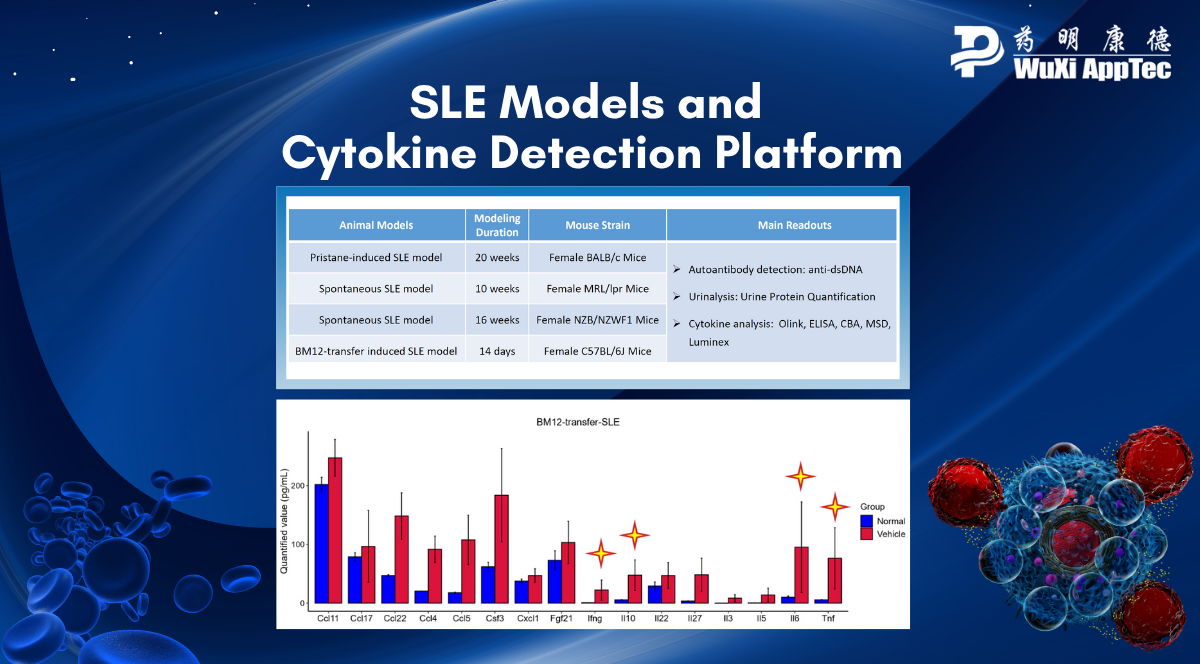
A key characteristic of SLE is the production of IgG autoantibodies, and a hallmark of the disease is the elevated presence of antibodies targeting nuclear components. To accelerate the development of effective treatments for SLE, WuXi Biology has established a series of animal models and a cytokine detection platform, empowering immune response assessments with accuracy, depth, and speed.

SLE Animal Models with Integrated Cytokine Detection Platform
Related Content
Introduction: RNA-based therapies are a frontier in biomedicine, with the potential to fundamentally change treatments for a wide range of...
VIEW RESOURCEEvidence suggests that type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with cognitive dysfunction and an increased risk of developing neurocognitive...
VIEW RESOURCE
