High-throughput FAMA Assay to Measure Humoral Immunity against Varicella-Zoster Virus
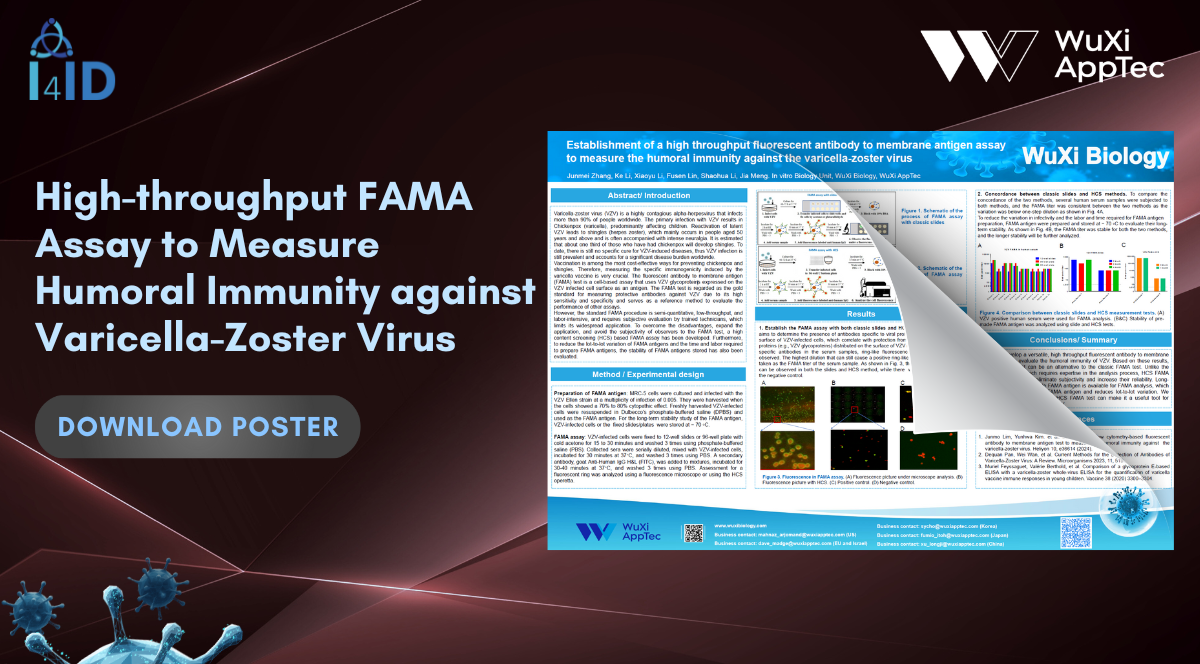
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a highly contagious alpha-herpesvirus that infects more than 90% of people worldwide. The primary infection with VZV results in chickenpox (varicella). Reactivation of latent VZV leads to shingles (herpes zoster) and is often accompanied by intense neuralgia. To date, there is still no specific cure for VZV-induced diseases.
The fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen (FAMA) test is a cell-based assay that uses VZV glycoproteins expressed on the VZV-infected cell surface as an antigen. The FAMA test is considered the gold standard for measuring protective antibodies against VZV.
However, the standard FAMA procedure is semi-quantitative, low-throughput, and labor-intensive, which limits its widespread application. To overcome these disadvantages and potentially expand its application, WuXi Biology presented a poster at I4ID 2025 describing the establishment of a high-throughput FAMA assay to measure the humoral immunity against VZV.

Poster_I4ID 2025_High-throughput FAMA Assay to Measure Humoral Immunity against Varicella-Zoster Virus
Related Content
From hematologic malignancies to solid tumors Introduction: Amid a surge of advancements in immunotherapy, T cell engager (TCE) therapy has...
VIEW RESOURCEAntibody-targeted therapies—including antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates (AOCs), and degrader-antibody conjugates (DACs)—are reshaping precision medicine by enabling highly selective delivery...
VIEW RESOURCE
