Combination Therapies in a Mouse MASH Model
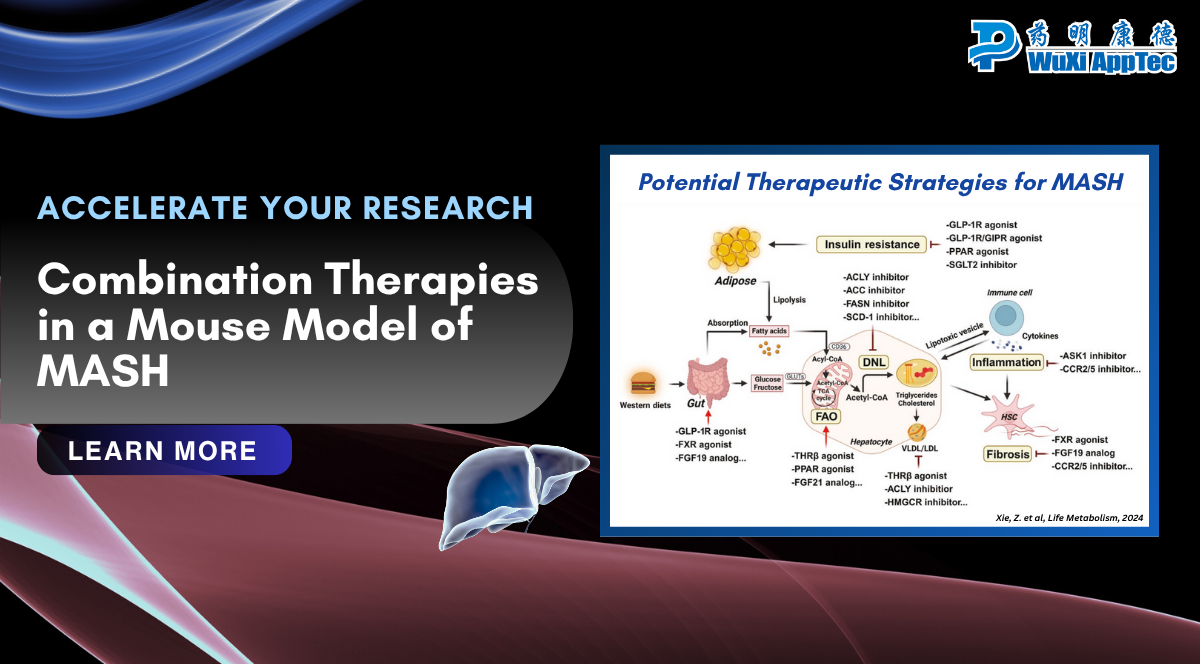
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), previously known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), is a serious liver disease. If left untreated, MASH can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. The main characteristics of MASH include fat accumulation, inflammation, fibrosis, and hepatocyte ballooning in the liver. The pathogenesis of MASH is complex and involves multiple interacting factors, often referred to as “multiple hits”.
This understanding of MASH pathogenesis has led to the realization that targeting multiple pathways with combination therapies has the potential to improve treatment efficacy. To support the development of novel therapies for metabolic diseases, WuXi Biology has established multiple steatosis/steatohepatitis models and evaluated combination therapies in these models.

Combination Therapies in a Mouse MASH Model
Related Content
Introduction: RNA-based therapies are a frontier in biomedicine, with the potential to fundamentally change treatments for a wide range of...
VIEW RESOURCEEvidence suggests that type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with cognitive dysfunction and an increased risk of developing neurocognitive...
VIEW RESOURCE
