Metabolic in vivo Models
Acute and chronic liver diseases are frequent and potentially life-threatening for humans. The underlying etiologies are diverse, ranging from viral infections, autoimmune disorders, and intoxications to imbalanced diets and others. Animal liver disease models are needed to mimic human liver diseases. WuXi Biology has established multiple animal liver disease models, including acute liver injury, obesity related liver damage, metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), including metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH), alcoholic steatohepatitis (ASH), liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). These models possess distinct features and etiology of human liver diseases to help evaluate the efficacy of lead compounds in relevant clinical liver diseases. They are designed to better understand the underlying mechanisms for new drugs to be used in the clinic.
Learn more about our hepatobiliary disease services platform
Diabetes & Diabetic Complications
| Spontaneous Diabetes | db/db mouse, ZDF rat |
| High-fat Diet-Induced Diabetes | Multiple species |
| Type 1 Diabetes Model | Streptozotocin (STZ) induction |
| Type 2 Diabetes Model | db/db mouse |
| Type 2 Diabetes Model | ob/ob mouse |
| Type 2 Diabetes Model | Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rat |
| Type 2 Diabetes Model | High-fat diet / STZ induction |
| Diabetic Nephropathy Model | Streptozotocin (STZ) induction |
| Diabetic Nephropathy Model | db/db mouse |
| Diabetic Neuropathic Pain | Chronic neuropathic pain |
| Diabetic Complications | Retinopathy (retina vascular leakage) |
| Diabetic Complications | Wound healing |
Obesity
| Spontaneous Obesity | (ob/ob mouse, aged CD-1 mouse, fa/fa rat) |
| Food Intake Screening | Multiple species |
| Diet-Induced Obesity (DIO) Model | High-fat diet (HFD) induction |
| Diet-Induced Obesity (DIO) Model | hGLP1r humanized mouse, high-fat diet (HFD) induction |
Dyslipidemia models
| Hyperlipidemia Model | High-cholesterol diet (HCD) induction |
| Hyperlipidemia Model | High-fat diet/cholesterol/fructose diet (HFD/WD) induction |
Liver disease and injury models

| Steatosis/ Steatohepatitis | — HFD-induced mouse MASLD model — HFD+CCl4-induced mouse MASH model — CDHFD-induced Rat/mouse MASH model — GAN Diet-induced mouse MASH model — STZ+HFD-induced mouse MASH model — MCD-induced mouse MASH model — Western diet-induced mouse MASH model — HFD+fruc/gluc in drinking water-induced mouse MASH model — CDAA diet-induced mouse MASH model — Ethanol liquid diet-induced rat/mouse ASH/ALD model — Diet and ethanol-induced MetALD model |
| Liver biliary tract diseases (autoimmune) | — ANIT diet-induced rat/mouse PBC model — DDC diet-induced mouse PSC model — Cholesterol and cholic acid-induced mouse cholelithiasis model |
| Drug/toxicant-induced liver injury | — APAP-induced mice acute liver Injury model — ConA-induced mouse acute liver Injury model — LPS/D-GalN-induced mouse acute liver Injury model |
| Fibrosis | — CCl4-induced mouse/rat liver fibrosis model — TAA-induced mouse liver fibrosis model — BDL-induced mouse/rat liver fibrosis model — HFCD-induced hamster liver fibrosis model |
| Cirrhosis | — CDHFD diet-induced rat cirrhosis model — CCl4-induced rat cirrhosis model |
| Liver failure | — APAP-induced mouse acute liver failure model — Liver ischemia and reperfusion mouse model |
| Hepatectomy liver regeneration | — Partial (70%) hepatectomy mouse model |
| Liver cancer | — Primary HCC & metastatic HCC — DEN+CCl4-induced mouse liver cancer model — CDX models — PDX models |
Endpoint Measurements
Clinical observation and physical examination
- Body weight, behavior, food intake, water intake, defecation
- Liver weight and spleen weight, ascite measurement, portal vein pressure
Biomarker analysis
- Serum ALT / AST analysis
- Gene expression and profiling (RT-PCR, microarray gene expression, miRNA)
- Protein and metabolite profiling (WB, ELISA, mass spectrometry)
- Hepatic hydroxyproline detection
Histology analysis
- H&E staining in liver tissues
- Sirius red staining and Masson Trchrome staining for collagen deposition and quantification in liver tissue
- α-SMA IHC staining and quantification in liver tissues
- Other related IHC staining for focused targets and markers
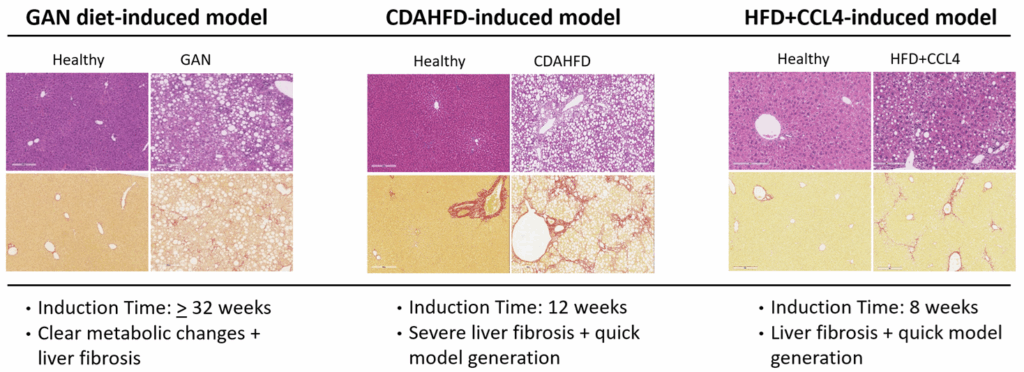
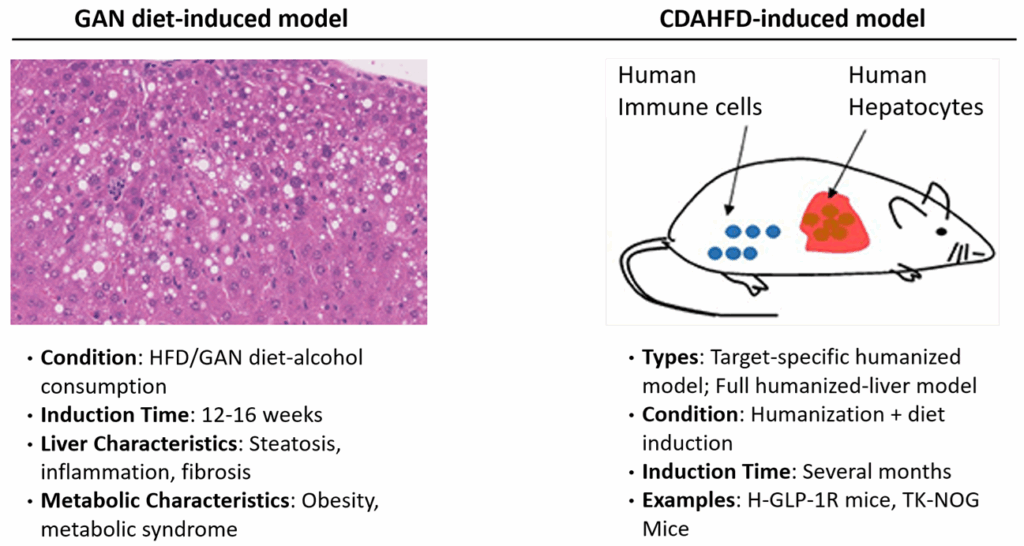
Widely Used Animal Models of MASH
Standard Models
- CDAHFD-induced mouse MASH model
- GAN diet-induced mouse MASH model
- Western diet-induced mouse MASH model
- HFD+CCL4-induced MASH Model
- CDAA-induced mouse MASH model
Innovative Characterization Matrix
Metabolism-Related Characterization
- Body Weight and Food Intake Test for metabolic condition monitoring.
- Body Composition Analysis for body fat and lean mass measurements.
- Energy Expenditure Analysis for activity, food/water intake, sleeping, and calorimetric assessment.
- Blood Glucose Level and Oral Glucose Tolerance for metabolic condition and insulin resistance test
- Serum Lipids (TC, TG, HDL, LDL) for metabolic condition test.
- Metabolic Cage Study for metabolic condition monitoring.
Liver-Related Characterization
- Liver-specific Biomarkers
— Serum transaminases: ALT, AST
— Hepatic lipids: TC, TG, HDL, LDL
— Biomarkers: TNF-α, IL-6, TIMP1, TBIL, GGT, Col1a1, α-SMA
— RNA level: TNF-α, IL-6, Col1a1, α-SMA
— Other novel markers - Histology
Liver size, H&E, MT, PSR, ORO, IHC, NAS, fibrosis score, quantitative histological analysis - DNA/RNA Level
PCR/qPCR, ddPCR, Exome Analysis, Transcriptome Analysis - Protein Level
Western blot, ELISA, proteomics; Protein and metabolite profiling (WB, ELISA, mass spectrometry) - Protein and Metabolite Profiling
WB, ELISA, mass spectrometry - Cellular
Flow cytometry, 3D liver organoid/spheroid - Ultrasound Examination
Real-time visualization and assessment of internal structures and functions

Case Study – In Vivo Evaluation of Key Drugs for MASH
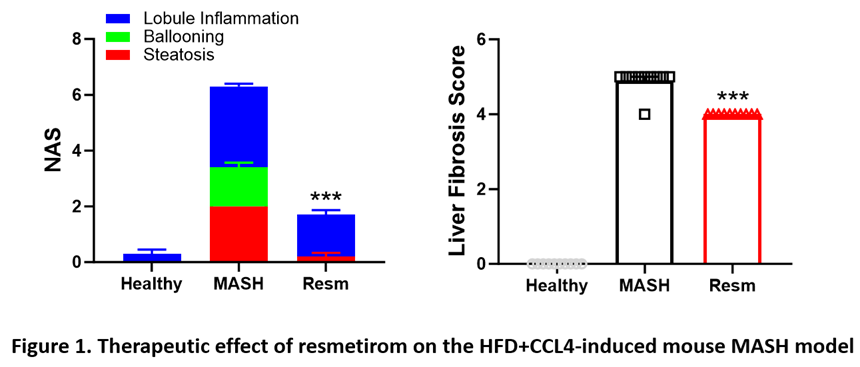
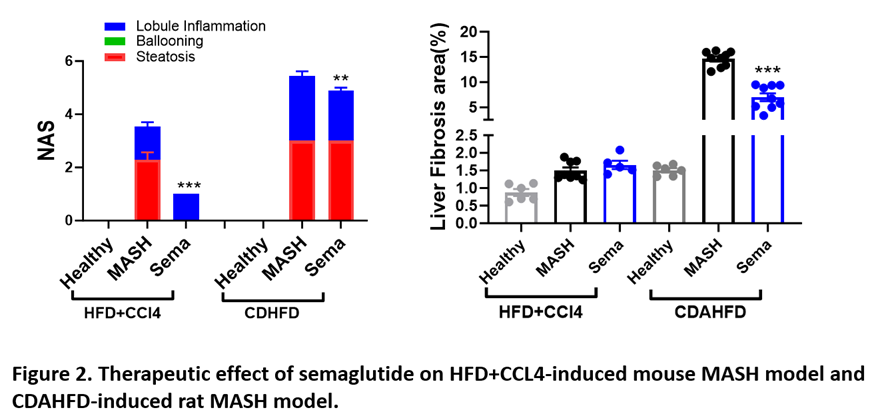
We developed two key MASH models in rodents: the high-fat diet (HFD)+CCL4-induced model and the CDAHFD-induced model. Additionally, we verified the therapeutic effects of two clinically approved MASH drugs, resmetirom and semaglutide, on these models. Our models accurately simulated the development of MASH and the therapeutic impact of these drugs in humans (Figures 1 and 2, below).
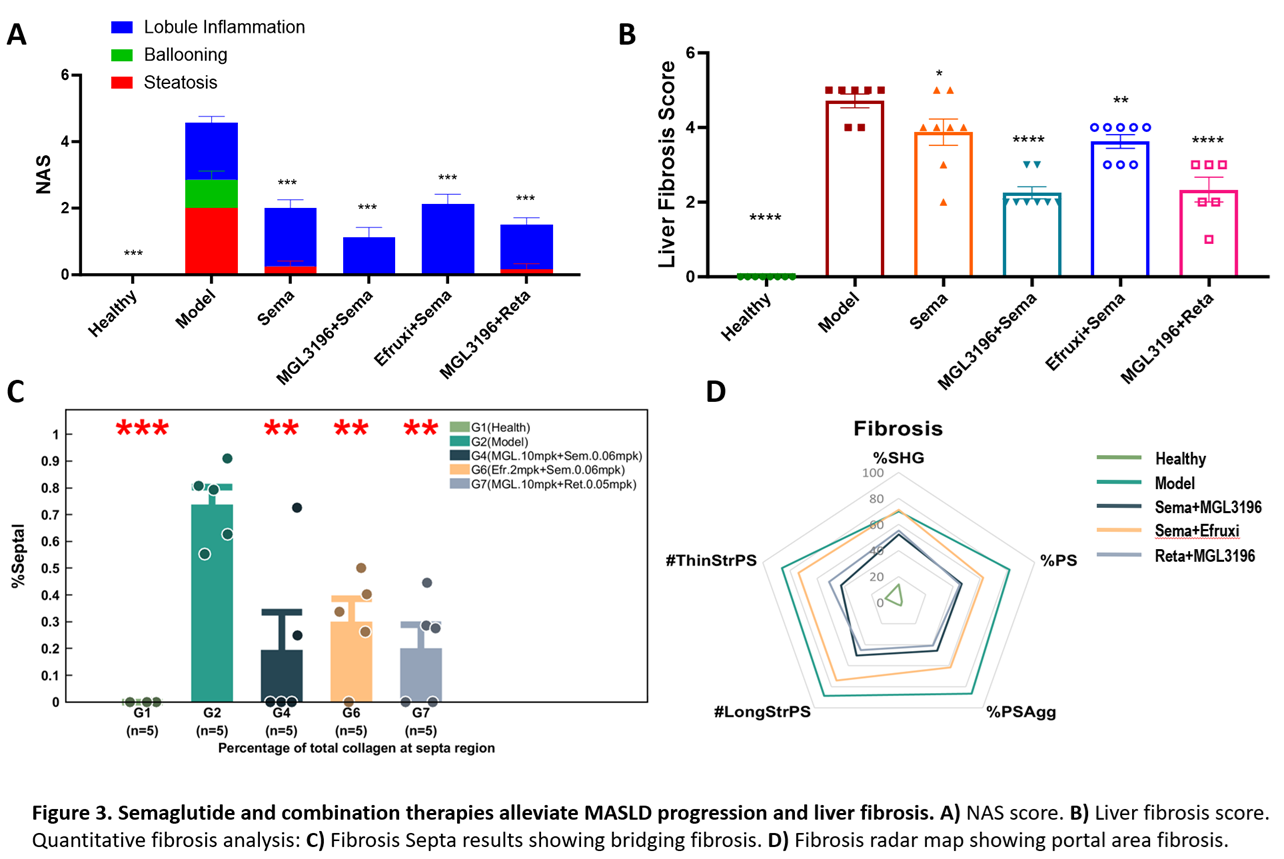
Case Study – In Vivo Evaluation of GLP-1RAs and Combination Therapies on MASH
We evaluated the efficacy of GLP-1 receptor agonists, in combination with other therapeutic agents, such as MGL3196 (also know as Resmetirom) and efruxifermin, in an HFD plus CCl4-induced mouse MASH model (Figure 3, below). While all treatments significantly reduced NAFLD activity score (NAS) and liver fibrosis scores. GLP1Rs+MGL3196 combinations showed the most substantial improvements, especially for fibrosis around the portal tract.