Identification of Tofacitinib, Filgotinib and Ruxolitinib on experimental Sjögren’s syndrome model in mice
Sjögren’s syndrome, which affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide, is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by leukocytic infiltration into the exocrine glands, such as the salivary and lacrimal glands. However, the pathological mechanism remains to be elucidated, and
novel treatments are urgently needed. Over the past decade, extensive progress has been made in the development of a Sjögren’s syndrome model in mice, which offers an invaluable tool to understand SjS pathogenesis.
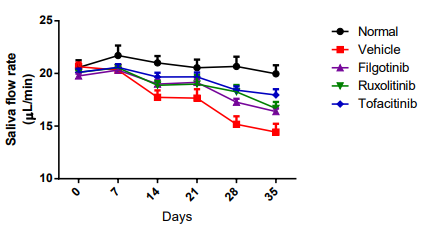
In this study, we identified the potential effect of Tofacitinib, Filgotinib and Ruxolitinib on the experimental Sjögren’s syndrome model in C57/BL6 mice from both in-life and ex-vivo studies. Our data suggest that Tofacitinib, Filgotinib and Ruxolitinib, three JAK inhibitors, are able to reduce the severity of Sjögren’s syndrome in mice, reducing auto-antibody production and promoting saliva secretion (thereby providing future direction of novel JAK inhibitors for treatment of Sjögren’s syndrome)

2021 AACR_Sjögren’s syndrome_1036_Ruiqing
Related Content
High-dimensional (HD) flow cytometry allows researchers to perform deep phenotyping of immune cells at the single cell level with increased...
VIEW RESOURCEReview of SITC 2023 Annual Meeting The 38th Annual Meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) was held...
VIEW RESOURCE
